Search Engine Marketing (SEM) & Search Engine Optimisation (SEO)
Having a website is great, but it will only perform if traffic is going to it.
There are two areas we recommend you should focus on: Pay-per-click advertising, and organic SEO. The latter means optimizing your website’s content and getting more backlinks to your website.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising
PPC advertising simply means that you pay every time someone clicks your ad, which leads them through to your website. Facebook and Google AdWords are two very popular websites that offer PPC advertising.
Facebook has one billion users now, which means advertising on the social network can be a great way to tap in to their circulation. We say ‘can’ because its users are just the average Joe – they are not business owners in most cases, therefore, if you were selling web design services like us (business-to-business), Facebook may be a waste of time and money because you would be targeting people who are just not interested.
Google AdWords is a tool that allows you to create ads to show up in Google searches, and then add keywords that trigger your ad to display. If you are selling books and are based in London, you may want to add ‘book shop London’ as one of your keywords. When someone types that phrase in, your ad will appear. Here’s what you should and shouldn’t be doing with Google AdWords:
Creating Your ads
If you offer property maintenance, for example, you may have two pages about landscaping and cleaning on your website. To start with, you need to create a campaign (a ‘folder’ that contains all of your ad groups, and allows you to set a daily budget for the campaign, as well as manage locations you want to target). Next, in the campaign you create, we recommend you create an ad group (a ‘folder’ that contains ads and keywords related to one product or service) for landscaping and then a separate ad group for cleaning. Next you need to create your ads, and aim to create between 2-3 variations to see what works best – it is always trial and error in AdWords in order to discover which techniques yield the most results.
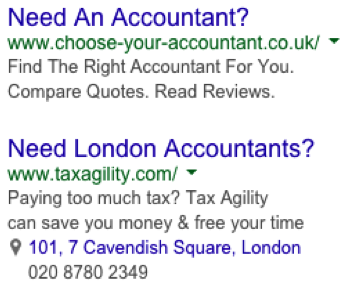
Ad text tips: Briefly tell people what you are offering. Include a call to action such as ‘call today’ or ‘contact us for a quote’. Let people know of any promotions or sales and make sure the page you direct people to tells them more about it. Also include a keyword (or two) in your ad text.
The ads to the left show up when you search for ‘accountants in London’. They both look relatively similar, and because of this, the advertisers will not be getting the best out of their efforts. When it comes to writing your ads, try and say something different, as it will separate you from the rest.
Once your ads are running, you can determine how well each of your ads are performing by comparing the amount of impressions (people who have seen your ad, but not clicked it) with the amount of clicks you are getting. If you have had 5,000 impressions but only received one click, this could suggest you need to improve your ad.
Keyword Research
Google has a great tool to make it easy to find keywords related to your products or services. It is called Keyword Planner and is located in the AdWords menu under Tools. You need to ‘search for new keyword and ad group ideas’ and complete the small form that appears. In this case, we want to find keywords for our ad group focused on landscaping, so in the first box relating to ‘your product or service’, we would type in one keyword phrase per line, such as ‘landscaping services London’ or ‘landscaping professionals London’. When you have entered the rest of the information, click the ‘get ideas’ button.
When the page has finished loading after clicking the ‘get ideas’ button, click the tab that says ‘keyword ideas’:
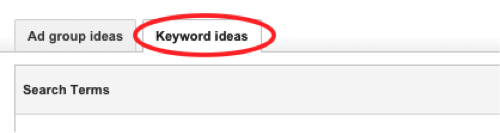
You should try to add the most relevant keywords to your ad group. In Keyword Planner we can see the most searched keywords relating to landscaping services is ‘garden ideas’ with 18,100 monthly searches. This might not be entirely relevant to landscaping services, however. If we did add that keyword, we may find that we will get a lot of clicks, but because people are looking for garden ideas and not landscaping services, it is very likely they will click away from the website as they didn’t find what they were looking for, and it would be a waste of money. Instead we can see ‘gardening services London’ is more relevant to our ad group, so we could add that.
Once you have added 10-20 keywords, it is time to do the same for any other ad groups you have set up.
Setting Budgets
When setting your budget, all you need to do is decide what your monthly budget is and then divide it by four, then by seven. If it’s £150, it works out at around £5.35 per day. Assuming you have one campaign with one or two ad groups, all you need to do is go in to the settings of your campaign and then type in your daily budget. NB: Each campaign requires its own daily budget.
While you are in the settings of your campaign, we recommend you set a maximum cost per click. This depends on how many clicks you want to get for your daily budget, and you need to keep in mind how expensive your keywords are. For example, for a daily budget of £5.35, 6 clicks per day might be all that I need. This works out at around £0.89 per click (daily budget divided by number of clicks you think you need). This means, my keywords will be bidding at a maximum of £0.89 per click, but this might not be enough to get to the first page of Google for some of your keywords, however, people do click past the first page of searches. In fact, they tend to browse up to three pages of Google searches, so you don’t always have to bid to be on first page all of the time. If you come back to your campaign after a few days and discover that you have not had many impressions or clicks, you may need to boost the maximum cost per click (CPC) and/or daily budget.
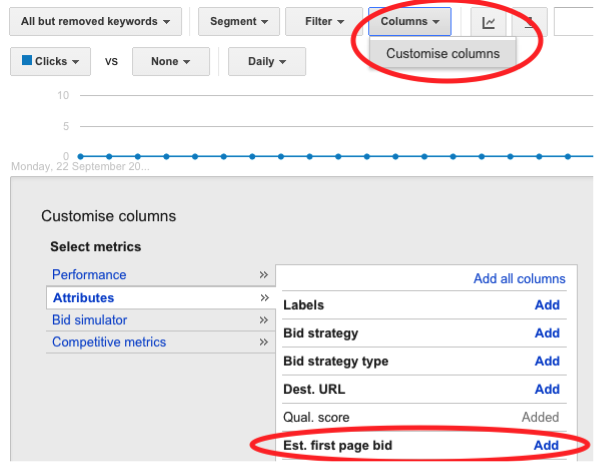
If you want to know what it costs to get to the first page of Google for each keyword, simply customise the columns in the Keywords tab and add ‘Est. first page bid’, and save changes (as shown below):
Improving Your Keywords
The more targeted your traffic is, the better. You don’t want to be showing up for keywords that are irrelevant to what you do. If we had a campaign containing an ad group focused on selling landscaping services, we wouldn’t want people searching for ‘gardening jobs’ to click our ad. This is where negative keywords & keyword types come in.
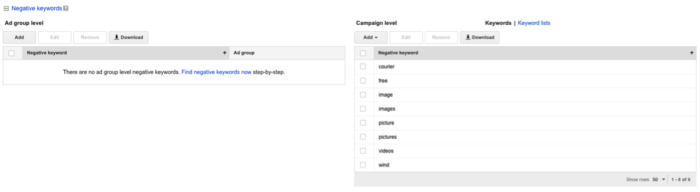
Negative keywords are keywords you don’t want your ads to show up for. For example, ‘windscreen repair’ might be a keyword a garage uses in their campaign, as they repair windscreens. What they don’t want is their ad to show for the keyword ‘wind’, or for synonym keywords related to the weather. When adding negative keywords, we recommend you do it at the campaign level, so that your negative keywords govern each ad group. To do so, click your campaign and then click the Keywords tab. At the very bottom of the keywords page you will see a blue link saying ‘Negative Keywords’. Click that, and add the keywords you don’t want to show up for in the Campaign Level section, as shown below:
Keyword Match Types determine how much leeway you give your keywords. There are four match types:
- Broad Match – when you add keywords to your ad groups, they will automatically be broad match keywords. What this means is your ads will automatically appear on relevant variations of your keywords, even if these terms aren’t in your keyword lists
- Exact Match – keywords show for exactly that phrase that is typed in, e.g. ‘landscaping services’, your ads will only show for that exact phrase.
- Phrase Match – if you add the keyword ‘tennis shoes’, phrase match will make your ad show for that exact phrase and include one or more keywords before or after it, such as ‘buy tennis shoes on sale’
- Broad Match Modifier – We recommend using this match type. It involves the use of the ‘+’ symbol. If you added the keyword ‘+shoe repairs’ to your ad group, the + symbol tells AdWords that the word ‘shoe’ must be present in people’s searches, before your ad displays. As there was no + symbol in front of the word ‘repairs’, this word can change to any synonyms such as ‘fix’ or ‘broken’. If there was no + symbol directly in front of the word ‘shoe’, it would be a broad keyword, and so your ads could show for ‘trainer repairs’ or ‘heel repairing’, for example.
AdWords has a great tool to see, over time, exactly what phrases people used to find and click your ad. This is especially useful because you can see if there are any irrelevant keywords creeping through, such as ‘jobs’. In the keywords tab, simply click Details, and then under Search Terms, click All:
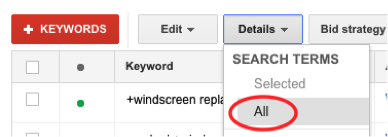
If you see any keywords in that list that are irrelevant, simply tick the checkbox to the left of the keyword, and click Add as Negative Keyword above the list. You can also add keywords that are relevant to your ad group.
Tips to Improve Your Ads
People browsing also use mobiles too to search Google. When you have created your ads, be sure to create mobile variations to accommodate for smaller screens. You can do so by ticking the ‘Mobile’ checkbox when you create ads. Sometimes AdWords replaces your second line with other features, so for mobile ads, try to have one sentence per line and keep each line at a maximum of 35 characters.
As people can tap a number to call from their mobile, instead of saying ‘get a quote’ as the call to action in your ad, it could say ‘call us free’.
Google have what’s called a Display Network as well as its search engine. This is where website owners dedicate sections of their websites to display ads. Google will show image and text ads here. Text ads are generally unattractive on these websites, and so people don’t tend to click them. We recommend changing the settings of your campaign type to be ‘Search Network only – All features’, until you create some image ads. This will mean your ads will only show in Google searches.
To create some image ads, you will need to ensure your campaign type is set to ‘search network with display select – all features’. This will reveal the ‘image’ option when you go to create a new ad, which, when clicked, will allow you to create an image ad using Google’s ad generator, or you can upload your own.
AdWords also has some extra features that you can use to give your ads an edge. These features are called Ad Extensions. Essentially, these features allow you to add your number, location, reviews, links to pages on your website and callouts to entice people to click your ads.
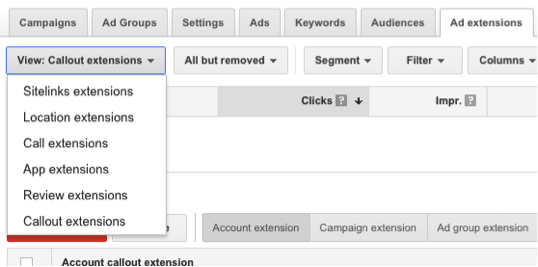
All the ad extensions are fairly self-explanatory, other than App extensions and Callout extensions. App extensions simply link directly to the download page of your app (if you have developed one). Callout extensions allow you to add another line of text below the description of your ad, but should be used to highlight a key offering, such as ‘free shipping – 24/7 customer service’.
We have a client that specialises in windscreen repairs and we discovered that the majority of people clicking their ads came from a mobile, presumably because they were out and about and used their mobile to search for companies that can fix their windscreens. A key thing to remember about mobile searches is that there is far less ad space per page. In mobile searches, ads only appear at the top and bottom of searches. For this reason, in the settings > devices page we added a bid adjustment of a 10% increase, in order for their ads to show a little higher on mobiles.
From time to time, AdWords may tell you that your Quality Scores are low. Quality score is the relevance of your ads in relation to your keywords. The content on the page of the website where people go to when they click your ad also comes into account. Avoid sending people to the home page of your website when they click your ad if possible. You may have an ad group focused on landscaping services, and you may have a page on your website telling them more about landscaping services – send them to the relevant page and your quality score will be higher. High quality scores also make the CPC cheaper (like a reward from Google for having a relevant ad showing up on relevant keywords, which leads through to a relevant page when clicked).
Your Website’s Content
Content is king. What we mean by that is if the wording on your website is unique (not copied & pasted from another website), well-written and laid out clearly using titles, you can expect better results than people who write ‘slap dash’ content. After you feel you have good content, the next thing to do is to optimise it for Google (nobody uses Bing or all the other search engines you used to know).
Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) is simply following Google’s suggestions to make your website better. Google believe in a seamless experience for their users – they type what they want, and the website they click on gives them exactly what they need in a clear and, most importantly, relevant way. To start with, we’re going to tell you what you should and shouldn’t be doing with your content:
Keyword-stuffing
After doing some keyword research, you now know what phrases you want to be found for in Google (e.g. book shop London). If you have a paragraph that reads:
“Black Books is a book shop in London that specialises in selling books in London. Our book shop is located in the heart of London, where we sell many books.”
The words ‘book’, ‘books’, ‘London’, ‘shop’ were used too many times in the space of two sentences. Visitors would hate reading this because it is keyword-stuffing. The trick is find 2-3 keywords that relate to each page of your website, and implement them into your content, whilst keeping the flow…
“Black Books are based in the heart of London. We sell a variety of novels, comics and other literature…”
This is a much better sentence because it has flow and the keywords are not deliberately repeated.
Meta Tags
When you do a Google search, the results on the left of the page (below the ads at the top) are called organic results. Organic simply means non-paid search results, and are extremely relevant to what a person is searching for.

The anatomy of each result starts with a blue title (which you use to click through to the website and briefly explains what the page is about), followed by the website address of the page, and a short description of the page. Meta tags allow you to determine what is displayed in your results that appear in searches. Any good website editor will give you the option to edit the title (which should be 50-60 characters) and description (which should be 150-160 characters) of each of your website’s pages, but every page must have a different title and description. If you exceed the character limits of your title and description meta tags, your search result will be ‘chopped off’ slightly. Alternatively, if you don’t put anything in the Meta tags of a page, Google will take a snippet of the wording on your page and insert it in the result, but most of the time it does a bad job of doing so and damages click-through-rate because the wording is not enticing.
Image ALT tags
ALT tags allow you to add a description of your images. Most website editors allow you to add ALT tags. If your image fails to load, or your website is being browsed by a disabled user who relies on software to read aloud your website’s content, ALT tags display your description of the image. For extra points, try naming the filenames of your images appropriately. Instead of ‘IMG_1234.jpg’, try ‘Macbeth-book.jpg’. Notice the keyword ‘book’ there too.
Navigation
Your website’s design comes in to play here. Your website must be usable on mobiles, tablets and desktops, and it must be easy for your users to get around your website. Small buttons and tiny text on any device just doesn’t cut it.
Hyperlinks should be distinguishable; they should not look like any other piece of ordinary text. Furthermore, the text you have hyperlinked should be descriptive – if you want people to contact you, instead of the link saying ‘click here to contact us’, you could say ‘get a free quote’ or ‘obtain a free estimate’. You should try to create some relevant hyperlinks on each page that link to other pages on your website (instead of just relying on a menu). If you sold cakes and a visitor was looking at your pricing page, you could provide a hyperlink to a photo gallery page of previous cakes you have made with the link saying ‘Check out our photo gallery’, for instance.
Link-building
Google ranks websites on their reputation. What that means is the more websites that link to your website, the better. BUT the websites that link to you must be relevant, and vice versa. A few years ago link trading was a big thing, but now it is frowned upon because people created a page called ‘links’ on their websites, where they dumped various links to irrelevant websites in return for a link on other websites. Google saw to this bad practice and put an end to it. Now, the best way to get links to your content is submitting your website to directories, people sharing your content on Facebook or writing blog posts and linking to your content, or any way that links to your content in a ‘clean’ way.
Domain name (www.yourdomain.co.uk)
The older, the better – older domain names tend to rank better as they tend to have a long track record of people linking to them. Age is just one factor, however. The actual name should have a keyword in it if possible that is relevant to what you do. Ours is www.web-marketing.co.uk and includes the keyword ‘marketing’. Doing this has been proven to help with ranking in Google.
You should also ensure that your domain name points to one address. For example, if you type yourdomain.co.uk in to a browser and it redirects to www.yourdomain.co.uk or vice versa, you have it set up correctly. Otherwise, Google sees two versions of your website at www.yourdomain.co.uk and yourdomain.co.uk and duplicate content can result in penalties.
When it comes to your individual pages, also be sure to give them a URL that is easy to type in, and SEO-friendly. Instead of ‘yourdomain.co.uk/directory1/directory2/about-us’, you should set the URLs to look like ‘yourdomain.co.uk/about’. The deeper it is to get to your page, the less value it has in searches, and the more arduous it is for people to type in.
Sitemaps
Sitemaps are a section of your website that should be easy for people to get to and use to see a list of your website’s pages. You should also create and submit a sitemap.xml file to Google using Google Webmaster Tools. This helps make it easier for Google’s ‘spiders’ to see what pages are on your website.
Robots.txt
This is a file that tells Google ‘spiders’ (or bots) what to do for certain pages. A privacy policy might not be something you want Google to show in its search results. If people land on that page, the chances are they will click back off because a privacy policy is not what they are looking for. For that reason, it is good practice to tell the bots to ignore those pages and focus on your other pages.
Call to Actions (CTAs)
Following Google’s guidelines can help your website rise in Google’s searches over a period of time – it is not an overnight job. But even if you reach page one of results, your website is the place where you pitch your products or services.
It’s great that you have populated your page with content, telling people what you are offering, but you can’t just lead the horse to water; you have to inspire it to drink too. Call to actions tells people what the next step is – it could be to call you or buy a product. CTAs are generally some instructive text at the bottom of a page where your visitors finish reading about your service, or above a form, telling them to do something. If you sell landscaping services, you may want people to call you to discuss a quotation. You can even look in to making a colourful and obvious button that leads to the contact page.
To Summarise
If you have managed to get this far, you should now understand that setting up a website and expecting the phone to ring is not the case. Your website must be easy to use on all devices (with a mobile-friendly website), have well-written content that is compliant with SEO guidelines and utilise call to actions. After, it is a case of using PPC marketing to quickly point some high quality traffic to your website, and continue optimising and reviewing your online presence to achieve the best results.